The Evolution and Importance of High Temperature Sensing Technology
The improvement of tall temperature sensors has revolutionized mechanical forms, especially in the domain of heater operations. These progressed gadgets have gotten to be the foundation of advanced fabricating, metallurgy, and materials handling businesses. The ability to accurately measure and control extreme temperatures has opened up new possibilities in product development and process optimization.
Advancements in Sensor Materials and Design
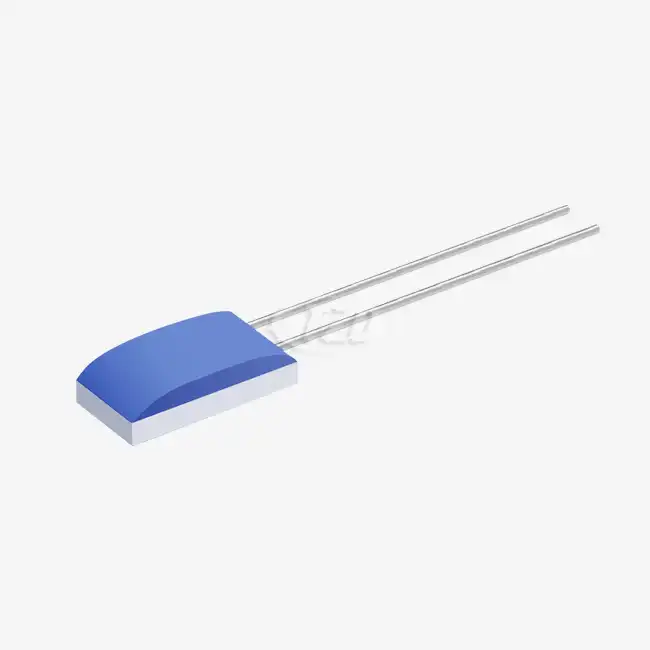
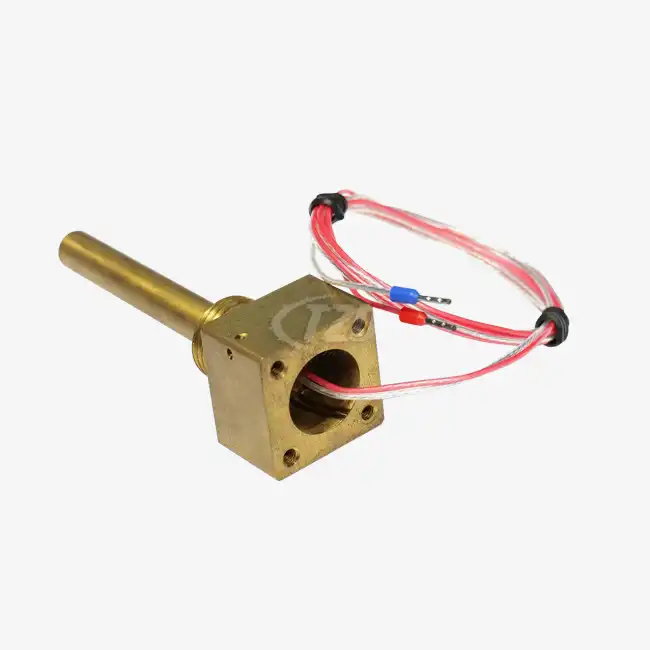
Recent years have seen significant advancements in high temperature sensor technology. Thin film platinum resistance thermometers, for instance, have emerged as a game-changer in the field. These sensors, with their compact dimensions (ranging from 1.2mm x 2.0mm x 1.0mm to 2.0mm x 2.3mm x 1.0mm), offer unprecedented precision in confined spaces. The utilize of platinum-nickel wire leads, with a length of 10 mm and a breadth of 0.2 mm, guarantees strength and unwavering quality indeed beneath extraordinary conditions.
The temperature coefficient (TCR) of 3850 ppm/°C in these sensors allows for highly accurate measurements across a wide temperature range. This level of precision is crucial for industrial furnaces where even slight temperature variations can significantly impact the final product quality. In addition, the capacity to withstand tall temperatures whereas keeping up a cover resistance of over 2 MΩ at 500°C talks to the strength of these sensors.
Expanding Applications in Industrial Settings
The versatility of modern high temperature sensors has expanded their applications beyond traditional industrial furnaces. These sensors now find use in diverse fields such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and advanced materials research. The ability to operate reliably in temperatures ranging from -200℃ to +850℃ makes them indispensable in processes requiring extreme heat or cold.
In industrial furnaces, these sensors enable precise control of heat treatment processes, ensuring consistent quality in metal fabrication, glass manufacturing, and ceramic production. The quick response time of up to 0.05 seconds allows for real-time adjustments, crucial in maintaining optimal furnace conditions and preventing overheating or underheating scenarios.
Enhancing Safety and Efficiency in Furnace Operations
Security is vital in mechanical situations, particularly when managing with high-temperature forms. Progressed temperature sensors serve as the to begin with line of defense against potential heater glitches that may lead to unsafe circumstances.
Preventing Overheating and Equipment Failure
One of the essential capacities of tall temperature sensors in mechanical heaters is to avoid overheating. Excessive temperatures can lead to material degradation, equipment damage, or even catastrophic failures. With their high accuracy (±0.01 Ω) and long-term stability (drift ≤ 0.04%), these sensors provide reliable data for temperature control systems to maintain optimal furnace conditions.
The robustness of these sensors, evidenced by their vibration resistance of 40g and impact resistance of 100g, ensures they can withstand the harsh environment inside industrial furnaces. This durability translates to fewer sensor failures and more consistent temperature readings, which is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted furnace operations.

Optimizing Energy Consumption
Productive vitality utilize is a key concern in mechanical operations, both for financial and natural reasons. High temperature sensors play a crucial role in optimizing furnace energy consumption. By providing accurate temperature data, these sensors enable precise control of heating elements, ensuring that energy is used only when and where it's needed.
The ability to operate with low currents (0.3 ~ 1 mA) while considering self-heating effects allows these sensors to provide accurate readings without significantly impacting the furnace's energy balance. This characteristic is especially important in large-scale mechanical heaters where indeed little advancements in vitality proficiency can lead to significant fetched investment funds and diminished natural affect.
Future Trends and Innovations in High Temperature Sensing
As mechanical forms proceed to advance, so as well does the innovation behind tall temperature sensors. The future of these critical components looks promising, with several emerging trends set to further enhance their capabilities and applications.
Integration with Industry 4.0 and IoT
The integration of high temperature sensors with Industry 4.0 and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is opening new avenues for furnace management and predictive maintenance. Advanced sensors can now communicate real-time data to centralized systems, allowing for remote monitoring and control of industrial furnaces. This connectivity enables predictive maintenance strategies, where potential issues can be identified and addressed before they lead to costly downtime or safety hazards.
Besides, the tremendous sum of information collected by these sensors can be analyzed utilizing fake insights and machine learning calculations. These analyses can reveal patterns and insights that lead to process optimizations, further improving furnace efficiency and product quality.
Advancements in Multi-sensor Integration
The trend towards multi-sensor integration is gaining momentum in the high temperature sensing field. By combining temperature sensors with other types of sensors (such as pressure or gas composition sensors), a more comprehensive picture of furnace conditions can be obtained. This holistic approach to monitoring allows for more nuanced control of industrial processes, leading to improved product consistency and reduced waste.
Companies at the forefront of sensor technology, like Xi'an Tongzida Technology Co., Ltd., are developing innovative solutions that incorporate multiple sensing capabilities into compact, reliable packages. These integrated sensor systems are particularly valuable in complex industrial processes where multiple parameters need to be monitored simultaneously.

Conclusion
High temperature sensors are indeed critical for industrial furnaces, serving as the eyes and ears of these vital manufacturing tools. Their ability to provide accurate, reliable temperature data in extreme conditions enables safer, more efficient, and more productive industrial processes. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and integrated sensing solutions to emerge, further revolutionizing the field of industrial furnace operations.
For those seeking cutting-edge high temperature sensing solutions for their industrial applications, Xi'an Tongzida Technology Co., Ltd. offers a range of advanced thin film platinum resistor sensors. With their commitment to quality and innovation, evidenced by their ISO9001, ROHS, and CE certifications, they are well-positioned to meet the evolving needs of the industry. For more information on their high temperature sensor offerings, interested parties can reach out to sales11@xatzd.com.